The figure Google’s Fusion: Hardware and Software Engineering shows that Google’s technology framework has two areas of activity. There is the software engineering effort that focuses on PageRank and other applications. Software engineering, as used here, means writing code and thinking about how computer systems operate in order to get work done quickly. Quickly means the sub one-second response times that Google is able to maintain despite its surging growth in usage, applications and data processing.
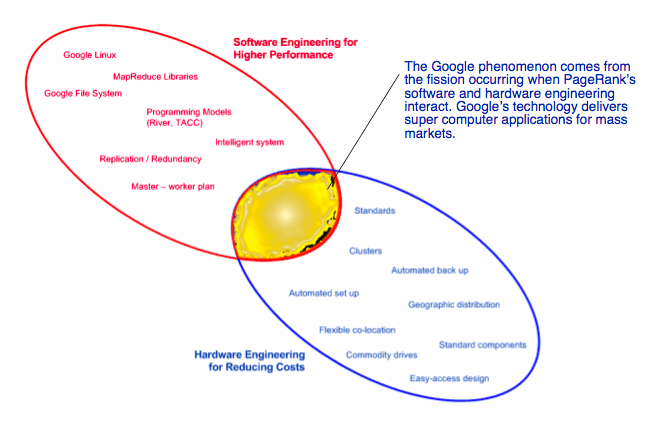
The other effort focuses on hardware. Google has refined server racks, cable placement, cooling devices, and data center layout. The payoff is lower operating costs and the ability to scale as demand for computing resources increases. With faster turnaround and the elimination of such troublesome jobs as backing up data, Google’s hardware innovations give it a competitive advantage few of its rivals can equal as of mid-2005.
…
How Google Is Different from MSN and Yahoo
Google’s technologyis simultaneously just like other online companies’ technology, and very different. A data center is usually a facility owned and operated by a third party where customers place their servers. The staff of the data center manage the power, air conditioning and routine maintenance. The customer specifies the computers and components. When a data center must expand, the staff of the facility may handle virtually all routine chores and may work with the customer’s engineers for certain more specialized tasks.
Before looking at some significant engineering differences between Google and two of its major competitors, review this list of characteristics for a Google data center.
1. Google data centers – now numbering about two dozen, although no one outside Google knows the exact number or their locations. They come online and automatically, under the direction of the Google File System, start getting work from other data centers. These facilities, sometimes filled with 10,000 or more Google computers, find one another and configure themselves with minimal human intervention.
2. The hardware in a Google data center can be bought at a local computer store. Google uses the same types of memory, disc drives, fans and power supplies as those in a standard desktop PC.
3. Each Google server comes in a standard case called a pizza box with one important change: the plugs and ports are at the front of the box to make access faster and easier.
4. Google racks are assembled for Google to hold servers on their front and back sides. This effectively allows a standard rack, normally holding 40 pizza box servers, to hold 80.
5. A Google data center can go from a stack of parts to online operation in as little as 72 hours, unlike more typical data centers that can require a week or even a month to get additional resources online.
6. Each server, rack and data center works in a way that is similar to what is called “plug and play.” Like a mouse plugged into the USB port on a laptop, Google’s network of data centers knows when more resources have been connected. These resources, for the most part, go into operation without human intervention.
Several of these factors are dependent on software. This overlap between the hardware and software competencies at Google, as previously noted, illustrates the symbiotic relationship between these two different engineering approaches. At Google, from its inception, Google software and Google hardware have been tightly coupled. Google is not a software company nor is it a hardware company. Google is, like IBM, a company that owes its existence to both hardware and software. Unlike IBM, Google has a business model that is advertiser supported. Technically, Google is conceptually closer to IBM (at one time a hardware and software company) than it is to Microsoft (primarily a software company) or Yahoo! (an integrator of multiple softwares).
Software and hardware engineering cannot be easily segregated at Google. At MSN and Yahoo hardware and software are more loosely-coupled. Two examples will illustrate these differences.
Microsoft – with some minor excursions into the Xbox game machine and peripherals – develops operating systems and traditional applications. Microsoft has multiple operating systems, and its engineers are hard at work on the company’s next-generation of operating systems.
…
Several observations are warranted:
1. Unlike Google, Microsoft does not focus on performance as an end in itself. As a result, Microsoft gets performance the way most computer users do. Microsoft buys or upgrades machines. Microsoft does not fiddle with its operating systems and their subfunctions to get that extra time slice or two out of the hardware.
2. Unlike Google, Microsoft has to support many operating systems and invest time and energy in making certain that important legacy applications such as Microsoft Office or SQLServer can run on these new operating systems. Microsoft has a boat anchor tied to its engineer’s ankles. The boat anchor is the need to ensure that legacy code works in Microsoft’s latest and greatest operating systems.
3. Unlike Google, Microsoft has no significant track record in designing and building hardware for distributed, massively parallelised computing. The mice and keyboards were a success. Microsoft has continued to lose money on the Xbox, and the sudden demise of Microsoft’s entry into the home network hardware market provides more evidence that Microsoft does not have a hardware competency equal to Google’s.
…
Yahoo! operates differently from both Google and Microsoft. Yahoo! is in mid-2005 a direct competitor to Google for advertising dollars. Yahoo! has grown through acquisitions. In search, for example, Yahoo acquired 3721.com to handle Chinese language search and retrieval. Yahoo bought Inktomi to provide Web search. Yahoo bought Stata Labs in order to provide users with search and retrieval of their Yahoo! mail. Yahoo! also owns AllTheWeb.com, a Web search site created by FAST Search & Transfer. Yahoo! owns the Overture search technology used by advertisers to locate key words to bid on. Yahoo! owns Alta Vista, the Web search system developed by Digital Equipment Corp. Yahoo! licenses InQuira search for customer support functions. Yahoo has a jumble of search technology; Google has one search technology.
Historically Yahoo has acquired technology companies and allowed each company to operate its technology in a silo. Integration of these different technologies is a time-consuming, expensive activity for Yahoo. Each of these software applications requires servers and systems particular to each technology. The result is that Yahoo has a mosaic of operating systems, hardware and systems. Yahoo!’s problem is different from Microsoft’s legacy boat-anchor problem. Yahoo! faces a Balkan-states problem.
There are many voices, many needs, and many opposing interests. Yahoo! must invest in management resources to keep the peace. Yahoo! does not have a core competency in hardware engineering for performance and consistency. Yahoo! may well have considerable competency in supporting a crazy-quilt of hardware and operating systems, however. Yahoo! is not a software engineering company. Its engineers make functions from disparate systems available via a portal.
…
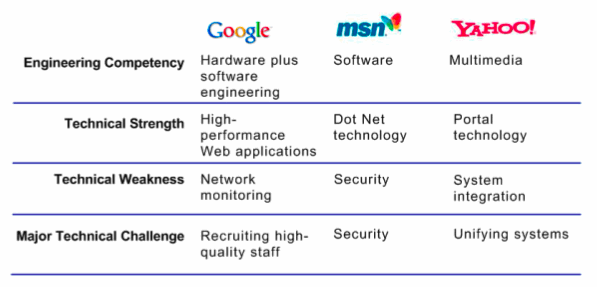
The figure below provides an overview of the mid-2005 technical orientation of Google, Microsoft and Yahoo.
The Technology Precepts
… five precepts thread through Google’s technical papers and presentations. The following snapshots are extreme simplifications of complex, yet extremely fundamental, aspects of the Googleplex.
Cheap Hardware and Smart Software
Google approaches the problem of reducing the costs of hardware, set up, burn-in and maintenance pragmatically. A large number of cheap devices using off-the-shelf commodity controllers, cables and memory reduces costs. But cheap hardware fails.
In order to minimize the “cost” of failure, Google conceived of smart software that would perform whatever tasks were needed when hardware devices fail. A single device or an entire rack of devices could crash, and the overall system would not fail. More important, when such a crash occurs, no full-time systems engineering team has to perform technical triage at 3 a.m.
The focus on low-cost, commodity hardware and smart software is part of the Google culture.
…
Logical Architecture
Google’s technical papers do not describe the architecture of the Googleplex as self-similar. Google’s technical papers provide tantalizing glimpses of an approach to online systems that makes a single server share features and functions of a cluster of servers, a complete data center, and a group of Google’s data centers.
…
The collections of servers running Google applications on the Google version of Linux is a supercomputer. The Googleplex can perform mundane computing chores like taking a user’s query and matching it to documents Google has indexed. Further more, the Googleplex can perform side calculations needed to embed ads in the results pages shown to user, execute parallelized, high-speed data transfers like computers running state-of-the-art storage devices, and handle necessary housekeeping chores for usage tracking and billing.
…
When Google needs to add processing capacity or additional storage, Google’s engineers plug in the needed resources. Due to self-similarity, the Googleplex can recognize, configure and use the new resource. Google has an almost unlimited flexibility with regard to scaling and accessing the capabilities of the Googleplex.
…
In Google’s self-similar architecture, the loss of an individual device is irrelevant. In fact, a rack or a data center can fail without data loss or taking the Googleplex down. The Google operating system ensures that each file is written three to six times to different storage devices. When a copy of that file is not available, the Googleplex consults a log for the location of the copies of the needed file. The application then uses that replica of the needed file and continues with the job’s processing.
…
Speed and Then More Speed
…
Google uses commodity pizza box servers organized in a cluster. A cluster is group of computers that are joined together to create a more robust system. Instead of using exotic servers with eight or more processors, Google generally uses servers that have two processors similar to those found in a typical home computer.
Through proprietary changes to Linux and other engineering innovations, Google is able to achieve supercomputer performance from components that are cheap and widely available.
…
… engineers familiar with Google believe that read rates may in some clusters approach 2,000 megabytes a second. When commodity hardware gets better, Google runs faster without paying a premium for that performance gain.
…
Another key notion of speed at Google concerns writing computer programs to deploy to Google users. Google has developed short cuts to programming. An example is Google’s creating a library of canned functions to make it easy for a programmer to optimize a program to run on the Googleplex computer. At Microsoft or Yahoo, a programmer must write some code or fiddle with code to get different pieces of a program to execute simultaneously using multiple processors. Not at Google. A programmer writes a program, uses a function from a Google bundle of canned routines, and lets the Googleplex handle the details. Google’s programmers are freed from much of the tedium associated with writing software for a distributed, parallel computer.
…
Eliminate or Reduce Certain System Expenses
Some lucky investors jumped on the Google bandwagon early. Nevertheless, Google was frugal, partly by necessity and partly by design. The focus on frugality influenced many hardware and software engineering decisions at the company.
…
Drawbacks of the Googleplex
…
The Laws of Physics: Heat and Power 101
…
In reality, no one knows. Google has a rapidly expanding number of data centers. The data center near Atlanta, Georgia, is one of the newest deployed. This state-of-the-art facility reflects what Google engineers have learned about heat and power issues in its other data centers. Within the last 12 months, Google has shifted from concentrating its servers at about a dozen data centers, each with 10,000 or more servers, to about 60 data centers, each with fewer machines. The change is a response to the heat and power issues associated with larger concentrations of Google servers.
The most failure prone components are:
- Fans.
- IDE drives which fail at the rate of one per 1,000 drives per day.
- Power supplies which fail at a lower rate.
Leveraging the Googleplex
…
Google’s technology is one major challenge to Microsoft and Yahoo. So to conclude this cursory and vastly simplified look at Google technology, consider these items:
1. Google is fast anywhere in the world.
2. Google learns. When the heat and power problems at dense data centers surfaced, Google introduced cooling and power conservation innovations to its two dozen data centers.
3. Programmers want to work at Google. “Google has cachet,” said one recent University of Washington graduate.
4. Google’s operating and scaling costs are lower than most other firms offering similar businesses.
5. Google squeezes more work out of programmers and engineers by design.
6. Google does not break down, or at least it has not gone offline since 2000.
7. Google’s Googleplex can deliver desktop-server applications now.
8. Google’s applications install and update without burdening the user with gory details and messy crashes.
9. Google’s patents provide basic technology insight pertinent to Google’s core functionality.





